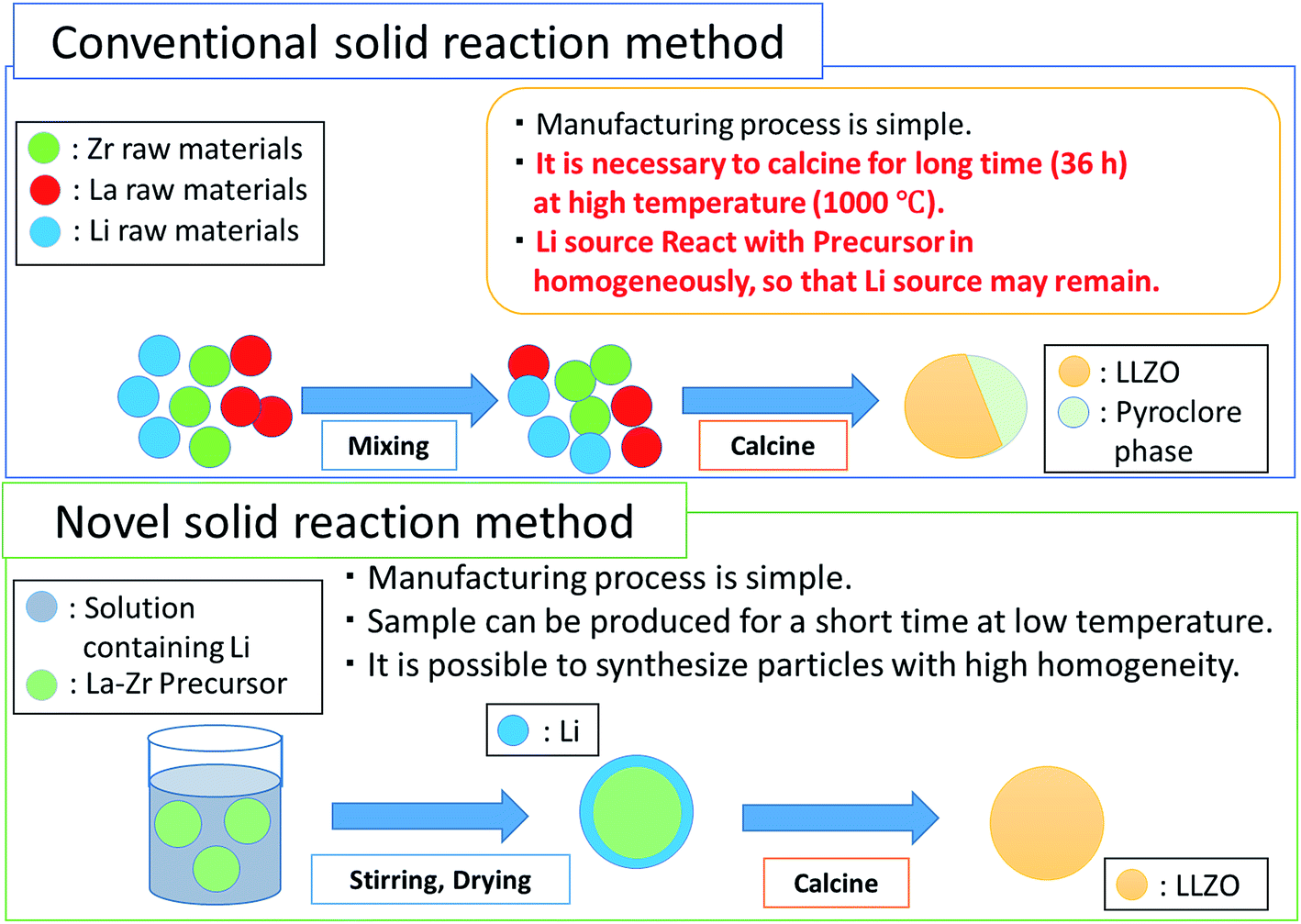
Solid State Reaction Ceramic Method

To obtain for example al 2 mo 3 o 12 from binary oxides it is necessary to have a local 1 3 stoichiometry of al 2 o 3 to moo 3.
Solid state reaction ceramic method. In this approach solid precursors are intimately grounded in stoichiometric quantities. The standard ceramic route the easiest way to make many solid state materials is direct reaction of their components at high temperatures pbo tio2 900oc pbtio 3 grind mix powdered reactants press into a pellet and heat. Engineering study materials 14 059 views 3 37. The solid state reaction route is the most widely used method for the preparation of polycrystalline solids from a mixture of solid starting materials.
High temperature must be used. Molten salt synthesis is a modification of the powder metallurgical method. The solid state reaction method or ceramic method is a well known processing route for obtaining thermodynamically stable phases at high temperatures through solid state diffusion. Solids do not react with solids at room temperature even of thermodynamics is favorable.
Solid state reaction method ssr. Ceramic method direct reaction of solids to form the final product in principle no decomposition is involved. Sol gel process steps for fabrication of ceramic matrix composites engineering study materials duration. Traditionally a high temperature ceramic synthesis also denoted as ceramic method or shake and bake is used to prepare inorganic solids.
The recently developed solid state reactive sintering ssrs method significantly simplifies the fabrication process for proton conducting ceramics by combining phase formation densification and grain growth into a single high temperature sintering step. Solids do not react together at room temperature over normal time scales and it is necessary to heat them to much higher temperatures often to 1000 to 1500 c in order for the reaction to occur at an appreciable rate. Ceramic powders are prepared from solid liquid and gas phases by various methods rahaman 2003. The characteristics of starting constituents are retained and the desired mixture is formed.